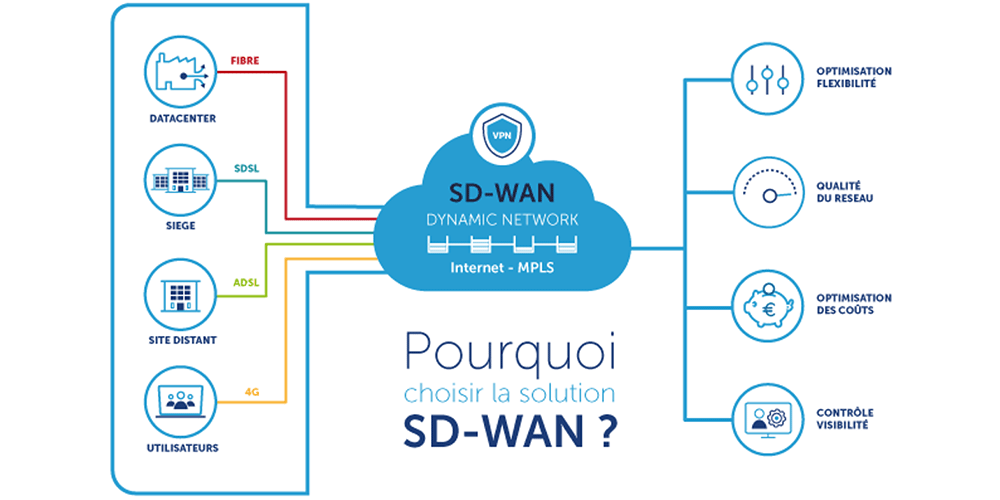
What is SD-WAN ?
The term Software-Defined refers to the emphasis on a product’s focus and the solution it provides originating from software rather than hardware, while WAN is the acronym for Software-Defined Wide Area Network, which is « a series of local area networks (LANs) or other networks that communicate with each other. » Combining these elements results in a technology that leverages software capabilities to bring cloud connectivity to multiple business branches through a simplified topology.
SD-WAN integrates a traditional hardware-based network model with an overlaid virtual network defined by software. This overlaid network, akin to a network on top of another network, is centrally managed and provisioned by a controller, eliminating the need for device-by-device network configuration and management. The underlying network, or data plane, is then responsible for processing and routing packets between devices.
The overlaid network can utilize various standard transport services across the network (acting in a « transport-agnostic » manner), including public Internet or 4G, 5G, and MPLS technologies. Depending on the performance of the underlying network transport, application-aware routing controls where and when an application uses a specific service to preserve the performance of real-time-sensitive applications.
Operations
SD-WAN operates to provide « application-aware routing in the WAN. » It acts as a private and flexible overlay network on any type of network transport, whether it’s public Internet, MPLS, or a combination of both. The brain of your SD-WAN continuously queries these multi-transport « overlay networks » to determine the optimal end-to-end network path, enhancing performance, resilience, and reducing costs for your business.
SD-WAN is a response to the growing need for a more efficient method to send traffic directly via the Internet from branch sites to trusted cloud and SaaS applications, while ensuring security compliance. It addresses this need by simplifying WAN architecture through a centralized control function that securely directs traffic directly between branches and to cloud service providers (CSPs).
SD-WAN advantages
There are several advantages to deploying SD-WAN in your enterprise network, promises that traditional or alternative configurations cannot fulfill. These include:
- Centralized Management: By shifting network control from individual branches and data center routers to a centralized tool, SD-WAN allows administrators to have an overview of the network. Policies can be applied to branches centrally, simplifying network administration.
- Cost Savings: Implementing SD-WAN can result in long-term cost savings, often exceeding 50% compared to MPLS configurations. As it enhances the reliability of WAN and Internet services, SD-WAN proves cost-effective by reducing unnecessary or complicated network paths and disruptions in network performance, ensuring business continuity.
- Improved Performance: By reducing latency and packet loss, SD-WAN can significantly enhance network performance. Employees experience faster speeds, whether working in the office or remotely from anywhere globally. SD-WAN also automatically routes critical traffic to links with higher bandwidth for improved application performance.
- Remote Access: The adoption of SD-WAN is growing significantly due to its cloud access capabilities. Remote employees can access cloud applications from multiple devices and locations, crucial in modern « work from anywhere » business models.
- Security Protocols: SD-WAN offers a decentralized security model with innovative security features such as firewalls, traffic filtering, and threat identification and management. SD-WAN connects branches to cloud-based applications via a secure and dedicated connection, eliminating the need to backhaul traffic to a data center first. Additionally, SD-WAN security can be managed from a centralized platform, mitigating risks associated with the public and potentially unreliable Internet.
Disadvantages of SD-WAN
The adoption and use of SD-WAN can also come with disadvantages for your business. Here are some considerations:
- Security Issues: Regarding its on-site security features, SD-WAN may fall short and lack effective built-in security measures. This means that a data breach occurring at one site could impact the entire enterprise. Security inefficiencies within your SD-WAN architecture could expose your business to threats such as network compromise and viruses, jeopardizing not only your company’s sensitive data but also that of your clients.
- Vendor Selection: Choosing the right SD-WAN provider for your business can be both time-consuming and challenging. Features, pricing, and contract terms can vary among providers, and some models may not be suitable for the specific operations of your business.
- Costs and Deployment Delays: The adoption of SD-WAN can be costly for businesses with tighter networking budgets, and the time required for deployment and replacing traditional infrastructure may be perceived as an obstacle.